Mineral processing – Milling
Practical Action
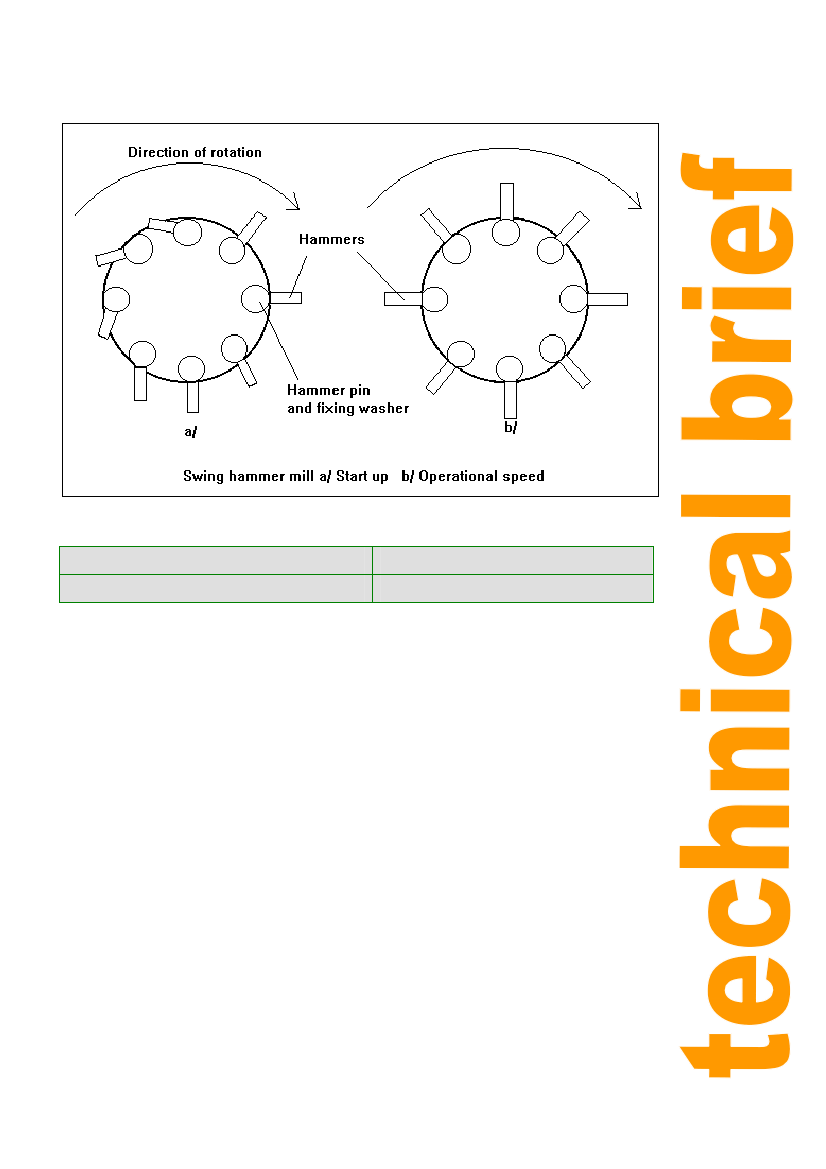
Figure 5: Types of hammer mills
Calcite
Barite
Table 8: Material suitability for hammer mills
Talc
Grain and other food stuffs
Pin, air classifying and turbo mills
Description:
A pin mill comprises two discs, one rotating and one stationary which are fitted with
intermeshing pins set in a concentric pattern. The charge is fed into the centre of the discs
and is broken down as it moves outwards through the pins which are moving at very high speed
- up to 20,000 rpm. The air classifying mill is similar in construction to the pin mill but
incorporates a built-in classifier. This type of mill produces a significant airflow through the
machine to aid with keeping temperature as low as possible. Oversize grains which pass
through the mill have to be recycled. Turbo mills use a similar concept but the rotating disc is
fitted with paddles or bars rather than pins. This rotating disc sits within a cage which is fitted
with grids, screens or breaker plates. The mill is configured in such a way as to produce the
desired particle size.
Characteristics:
Pin mills are capable of very fine grinding without the need for screens and provide a uniform
product size. Air classifying mills are used where the product is temperature sensitive. They
are widely used in the pharmaceutical and fine chemical industries. They are suitable for
relatively soft materials (below Moh 3) and for small quantities of material. Wear on the pins is
significant if used continuously.
8